Cycle 5 (2015 Deadline)
Seamless solar PV integration in Moroccan buildings
PI: Mounir Ghogho (mounir.ghogho@uir.ac.ma), International University of Rabat
U.S. Partner: Paul Flikkema, Northern Arizona University
Project Dates: December 2016 - May 2022
Project Overview
A high density of installed solar photovoltaic (PV) systems poses challenges, including excessive ramps and peaks of solar power into low-voltage grids that may cause blackouts. The penetration of roof-mounted PV in Moroccan buildings is still very low, despite estimated potential power generation of 10 TWh (terawatt hours), or 40% of the country's total electricity consumption. Two main obstacles are capital investment cost, as no financial incentives are offered yet by the government, and a conservative attitude of the national electricity utility company toward PV injection in the low-voltage grid.
To optimally design a battery-supported PV system, realistic household load profiles in Morocco must be used. This PEER project built a statistically significant dataset of household electricity consumption profiles in Morocco and made it available as open data to the scientific community. Team members analyzed the data using machine learning to assess and classify power quality at the household level. Through their open data and outreach activities, the project team aimed to contribute to the promotion of clean energy adoption in buildings and the modernization of the Moroccan electric grid.
Final Summary of Project Activities
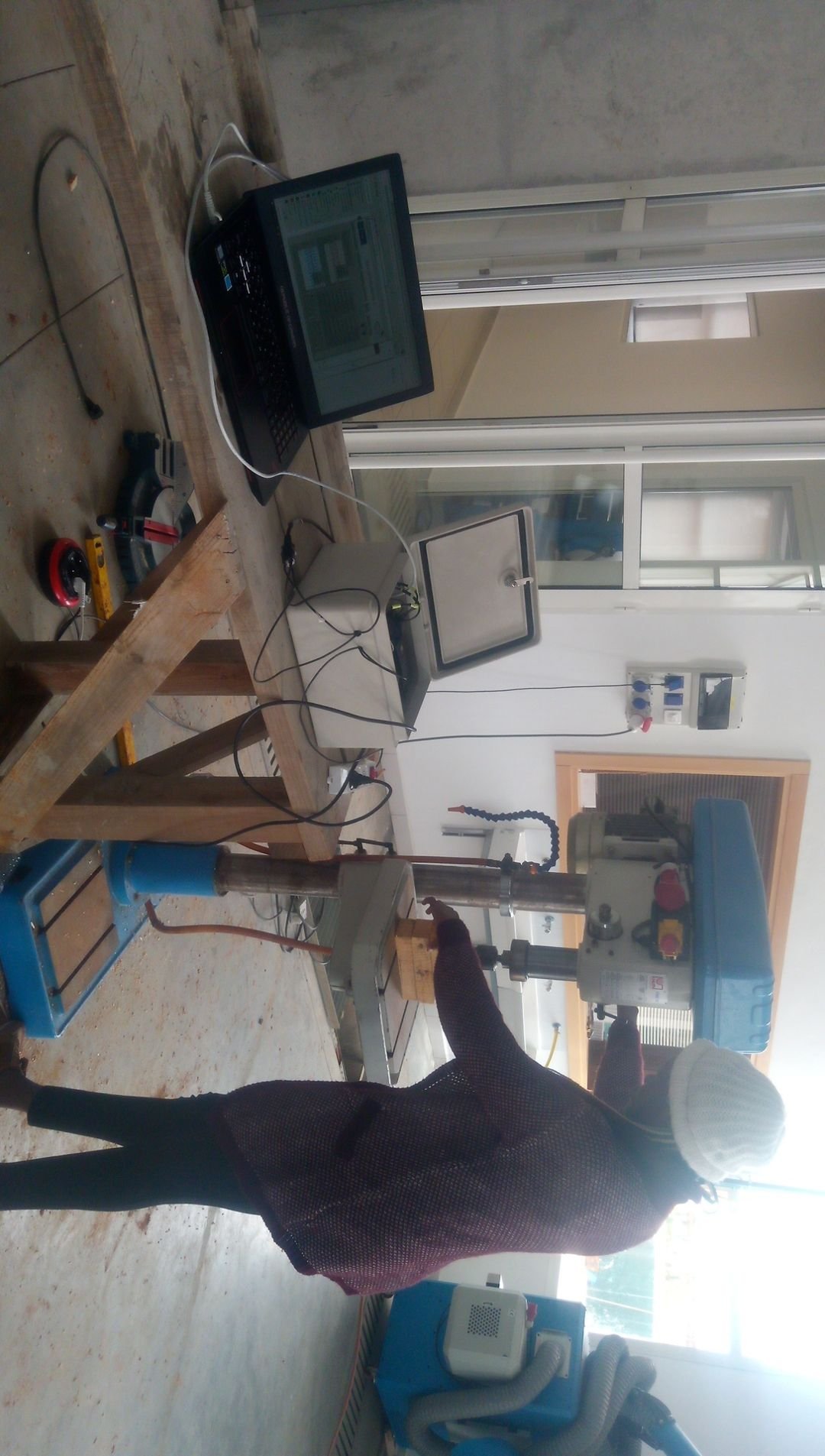
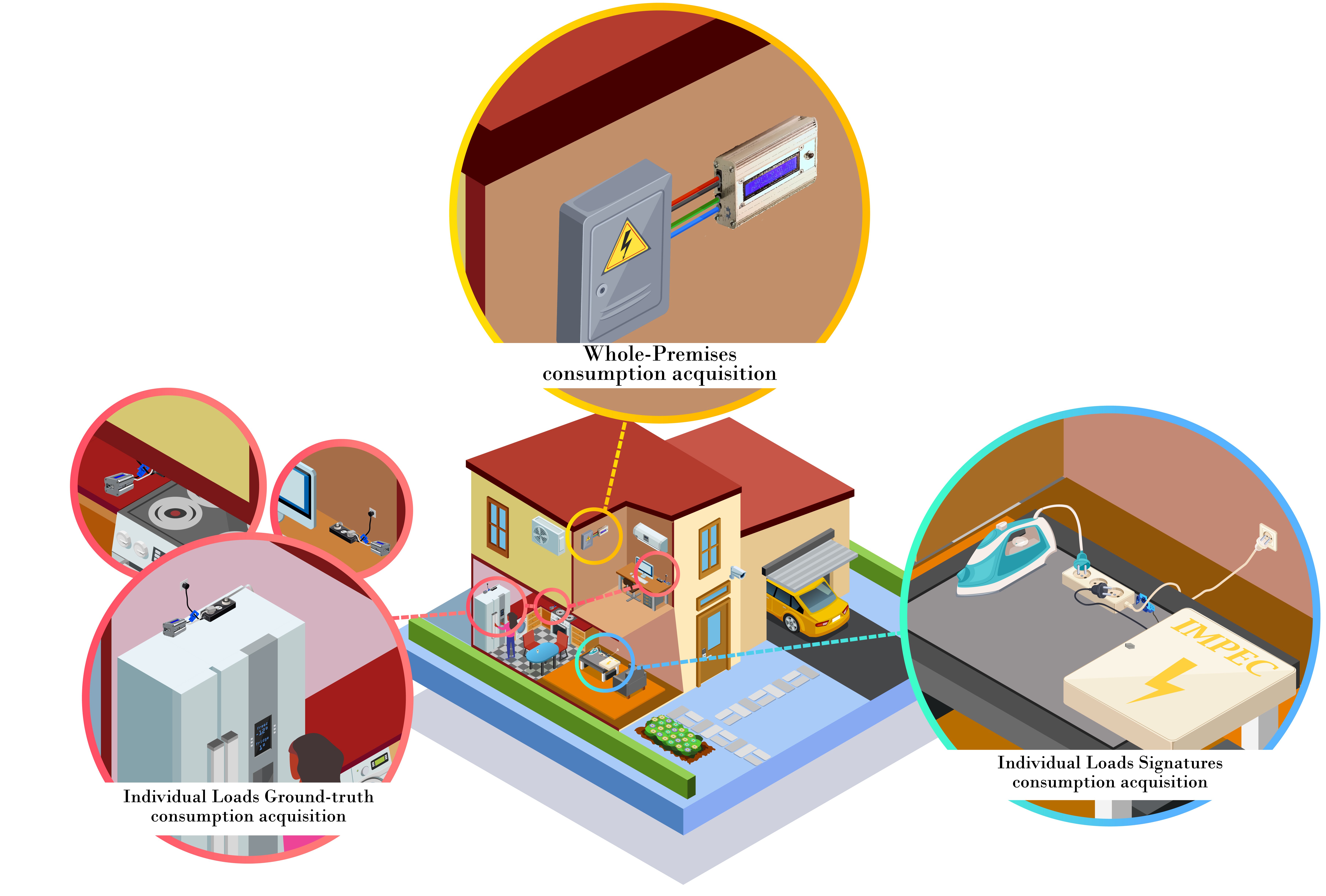
Dr. Ghogho and his colleagues developed an integrated system for monitoring and processing of electricity consumption in both residential and industrial settings. They used this system to build a dataset of Moroccan households’ electrical consumptions, with the aim of determining typical energy consumption profiles of households of different types (apartments, semi- detached, and detached houses) and different socioeconomic status, developing load forecasting algorithms, creating electrical consumption disaggregation algorithms, and determining power consumption by individual appliances.
The team’s dataset includes the electricity consumption of 13 households of different socioeconomic status over the course of the project, as well as power consumption data for the individual appliances used in the households. The dataset is the first of its kind in Africa and could be used by both researchers and engineers for various projects, including the design of PV systems for residential buildings.
From this dataset and others, the PEER team developed a novel method for multi-horizon forecasting of residential electricity consumption, with a maximum prediction horizon of 24 hours and an energy management system (EMS) for a microgrid consisting of a grid-tied building, PV panels, and a battery. The performance of the EMS on the system was tested via simulations and designed to maximize the benefits of the residential smart grid without injecting energy into the electrical grid.
The PI and PEER team presented their project and findings at several national and international events, including The Mediterranean Symposium on Smart City Applications. They also developed strong ties with IRESEN, a public agency in charge of promoting research and development in renewable energy in Morocco. IRESEN was particularly interested in datasets on electricity consumption in Morocco, and the PEER team presented the merits of a battery-backed PV system in Morocco’s urban areas.
As a result of the project, the co-PI received a $45,000 grant to continue work on energy consumption in smart cities, funded by a French-Moroccan cooperation program), and the PI received a $335,000 grant to work on solar PV-powered electric vehicle charging systems, funded by the Rabat-Sale-Kenitra regional government.
Publications
Mohamed Aymane Ahajjam, Daniel Bonilla Licea, Mounir Ghogho, and Abdellatif Kobbane. 2022. Experimental Investigation of Variational Mode Decomposition and Deep Learning for Short-Term Multi-Horizon Residential Electric Load Forecasting. Applied Energy 326, 119963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119963
Mohamed Aymane Ahajjam, Chaimaa Essayeh, Mounir Ghogho, and Abdellatif Kobbane. 2021. On Multi-Label Classification for Non-Intrusive Load Identification Using Low Sampling Frequency Datasets. Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), IEEE, Glasgow, May 17-20, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/i2mtc50364.2021.9460059
Mohamed Aymane Ahajjam, Daniel Bonilla Licea, Mounir Ghogho, and Abdellatif Kobbane. 2020. IMPEC: An Integrated System for Monitoring and Processing Electricity Consumption in Buildings. Sensors 20(4): 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041048
Mohamed Ayman Ahajjam, Daniel Bonilla Licea, Chaimaa Essayeh, Mounir Ghogho, and Abdellatif Kobbane. 2020. MORED: A Moroccan Buildings’ Electricity Consumption Dataset. Energies 13(24): 6737. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13246737
Mohamed Aymane Ahajjam, Daniel Bonilla Licea, Mounir Ghogho, and Abdellatif Kobbane. 2020. Electric Power Quality Disturbances Classification Based on Temporal-Spectral Images and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. 2020 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing: 1701-1706. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWCMC48107.2020.9148438
Daniel Bonilla Licea, Moisés Bonilla, Mounir Ghogho, Samson Lasaulce, and Vineeth S. Varma. 2020. Communication-Aware Energy Efficient Trajectory Planning with Limited Channel Knowledge. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 36(2): 431-442. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2019.2948801
Daniel Bonilla Licea and Mounir Ghogho. 2018. Low Complexity Closed-Loop Energy Manager for a Grid-Tied PV System with Battery. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm). https://doi.org/10.1109/SmartGridComm.2018.8587425
Back to PEER Cycle 5 Grant Recipients
|